The Union Parliament of Myanmar passed Tax Administration Law (“TAL”) on 7th June 2019 as a Pyidaungsu Htuttaw Law No. 20/2019. It was signed by the President of Myanmar on the same day. It will enter into force on 1st October 2019. The TAL is one of the most significant tax legislations. It aims to set out the administrative procedures. It governs the income tax, commercial tax, special goods tax and other types of tax under supervision of the Director-General (“DG”) of the Inland Revenue Department (“IRD”). Its major provisions are on the followings:-
- The IRD is authorized to issue public rulings and advance rulings to tax payers for consistency in implementation of the relevant tax laws and for using as guidelines for interpretation of relevant tax laws.
- The anti-avoidance provision has been adopted to be imposed on taxpayers for their avoidance of tax payments. The DG is authorized to impose the tax based on the economic substance of the tax payer.
- A taxpayer is required to maintain its documents related to tax liabilities that include purchase orders, invoices, daily records, financial statements and business contracts.
- The tax assessment and audit period has been extended to 6 years after the end of the relevant assessment year or 12 years in case of tax deception.
- A tax declaration is specified, including its submission period and a request for extension of the submission period. The DG or authorized officers can request for relevant information from the tax payer or inspect any documents of the tax payer by a prescribed manner.
- An appeal by a taxpayer can be filed with the DG within 30 days after receiving a notice of the applicable tax if the taxpayer finds that the decision or tax imposed on it is incorrect. A further appeal can also be filed with the Tax Tribunal within 90 days if the tax payer is not satisfied with the result of the first appeal. A further appeal with the Union Supreme Court is possible. The burden of proof is on the taxpayer.
- A taxpayer must notify the IRD on any changes to its business nature, company name and address in writing within 15 days after the changes for commercial tax and special goods tax matters and within one year after the changes for income tax matters.
- A taxpayer can request a tax clearance certificate from the IRD to confirm that the tax payer is cleared of tax liabilities.
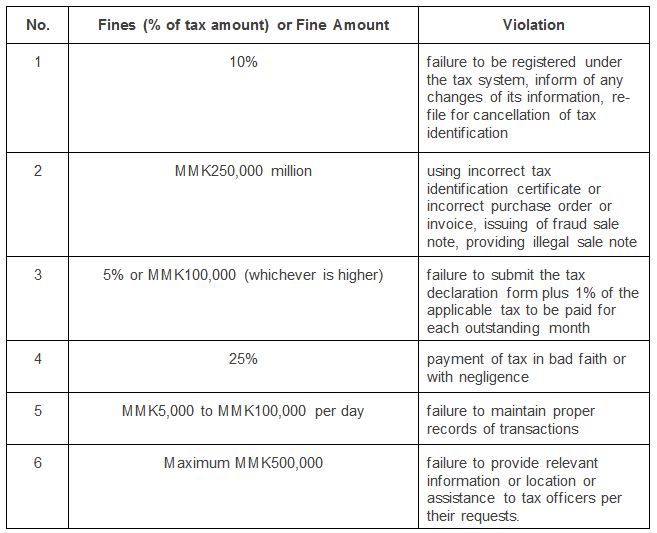
- The fines applicable to a tax payer under the TAL include:
AUTHOR
 Senior Partner | bangkok
Senior Partner | bangkok Partner | yangon
Partner | yangon
The information provided in this document is general in nature and may not apply to any specific situation. Specific advice should be sought before taking any action based on the information provided. Under no circumstances shall LawPlus Ltd. and LawPlus Myanmar Ltd. or any of their directors, partners and lawyers be liable for any direct or indirect, incidental or consequential loss or damage that results from the use of or the reliance upon the information contained in this document. Copyright © 2016 to 2020 LawPlus Ltd.
Tax






